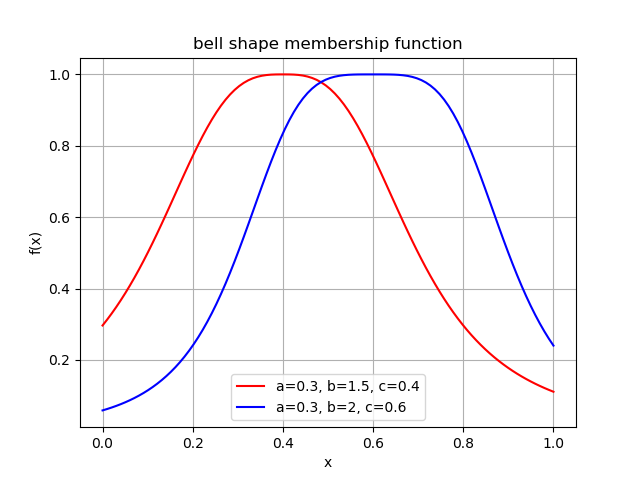
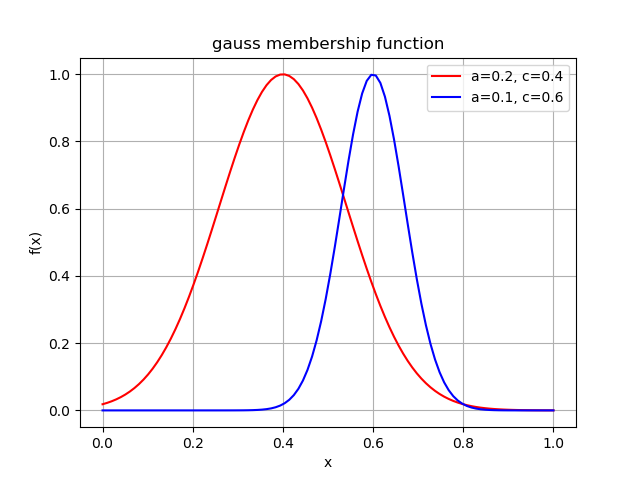
2.2. 隶属函数¶
2.2.1. 什么是隶属函数¶
隶属函数 (Membership Function) 是模糊集合的核心概念, 反映了元素属于模糊集合的隶属度(Membership Degree, Membership Grade). 模糊集的隶属函数与明确集的指示函数(Indicator function)或特征函数(characteristic function)相对应.
The membership function of a fuzzy set is a generalization of the indicator function in classical sets. In fuzzy logic, it represents the degree of truth as an extension of valuation. Degrees of truth are often confused with probabilities, although they are conceptually distinct, because fuzzy truth represents membership in vaguely defined sets, not likelihood of some event or condition. Membership functions were introduced by Zadeh in the first paper on fuzzy sets (1965). Zadeh, in his theory of fuzzy sets, proposed using a membership function (with a range covering the interval (0,1)) operating on the domain of all possible values.
对于任意集合 \(\mathbb X\), 其上的 隶属函数 为从 \(\mathbb X\) 到区间 \([0, 1]\) 的任意映射函数 \(f: {\mathbb X} \rightarrow [0, 1]\) .
隶属函数与模糊集合一一对应, 模糊集合 \({\mathbb A} \subset {\mathbb X}\) 的隶属函数通常表示为 \(\mu_{\mathbb A}\) , 对于 \(x\in{\mathbb X}\), \(\mu_{\mathbb A}(x)\) 表示隶属度, \(\mu_{\mathbb A}(x) = 0\) 意味着 \(x\) 不属于 \(\mathbb A\) ; \(\mu_{\mathbb A}(x) = 1\) 意味着 \(x\) 完全属于 \(\mathbb A\); \(0 < \mu_{\mathbb A}(x) < 1\) 意味着 \(x\) 部分属于 \(\mathbb A\) .
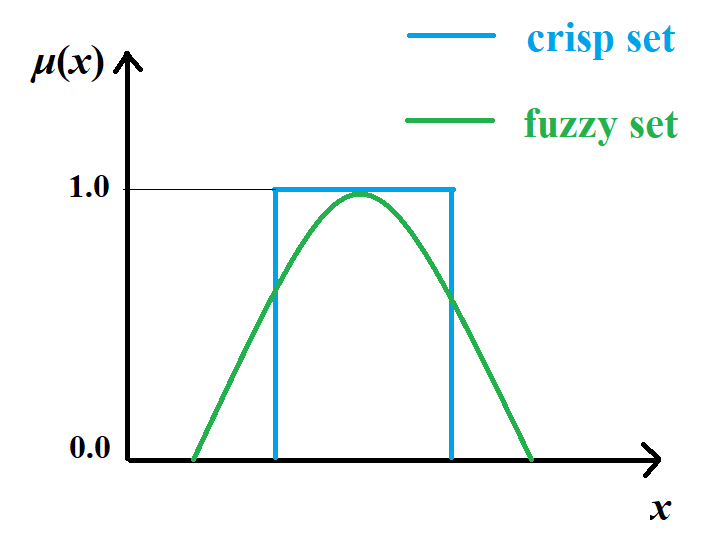
图 2.2 Membership Function of crisp set(blue) and fuzzy set (green).¶
Membership Function of crisp set and fuzzy set.