4.4. 正则化成像方法¶
4.4.1. 正则化成像¶
SAR imaging process can be formulated as
where, \({\bm s}\) is the \(MN\times 1\) recieved SAR raw data vector in phase history domain, \(\bm g\) is the \(HW \times 1\) reflection vector of scene, and \(\bm A\) represents the the mapping from scene to SAR raw data.
Given \(\bm s, \bm A\) , regularization methods try to reconstruct \(\bm g\) by minmizing
where, \(\lambda\) is the balance factor, and \(|\cdot|_p\) is the \(\ell_p\) norm.
Note that, if \({\bm s, A, g} \in {\mathbb C}\) , the problem changes to
so we have:
4.4.2. 实验与分析¶
实验说明¶
仿真场景大小: \(32 \times 32\)
回波矩阵大小: \(32 \times 32\)
稀疏表示字典: 无,
DCT,DWT优化方法:
Lasso,OMP
仿真点目标场景图及仿真生成点SAR原始数据幅度与相位图如下:
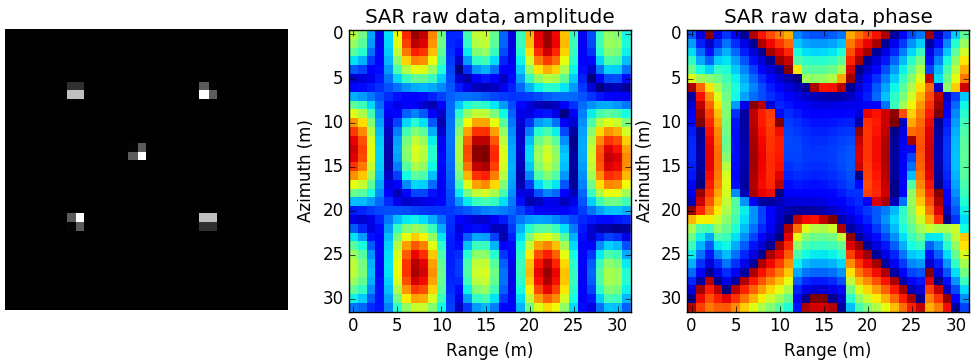
图 4.55 仿真点目标场景图, 仿真SAR原始数据幅度相位图¶
仿真船只场景图及仿真生成点SAR原始数据幅度与相位图如下:
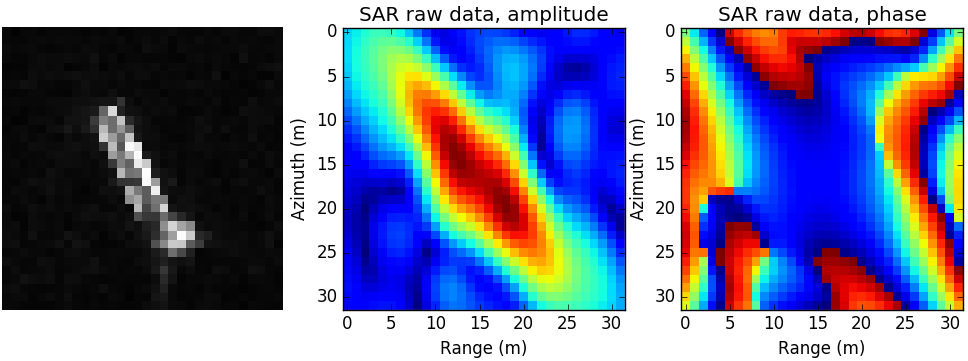
图 4.56 仿真船只场景图及仿真生成点SAR原始数据幅度与相位图如下¶
仿真荷花场景图及仿真生成点SAR原始数据幅度与相位图如下:

图 4.57 仿真荷花场景图及仿真生成点SAR原始数据幅度与相位图如下¶
实验结果¶
点目标结果
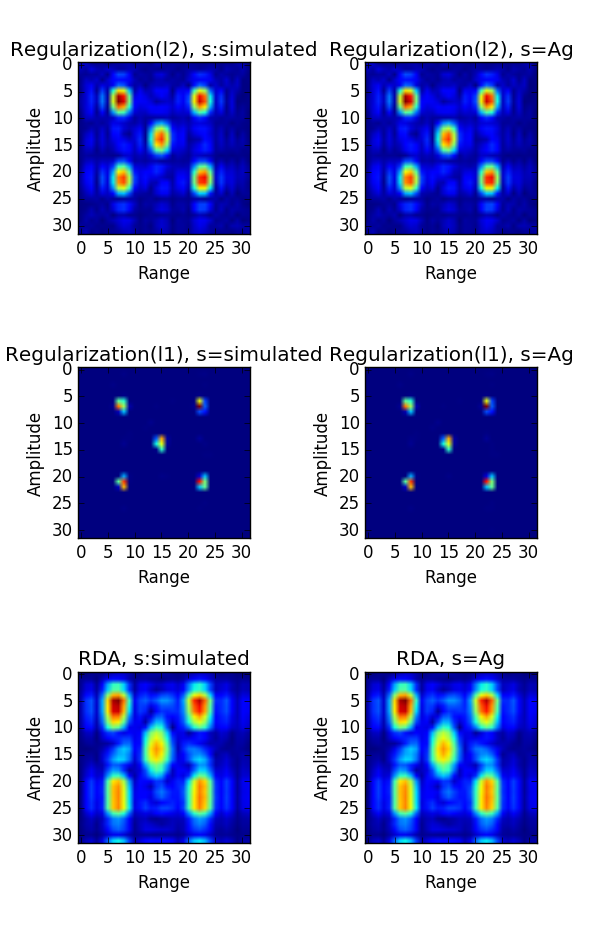
图 4.58 Imaging result of \(\ell_1, \ell_2\) regularization and RDA. \(\lambda=0.001\) , max iter 1000¶

图 4.59 Imaging result of \(\ell_1, \ell_2\) regularization and RDA. \(\lambda=0.001\) , max iter 1000¶
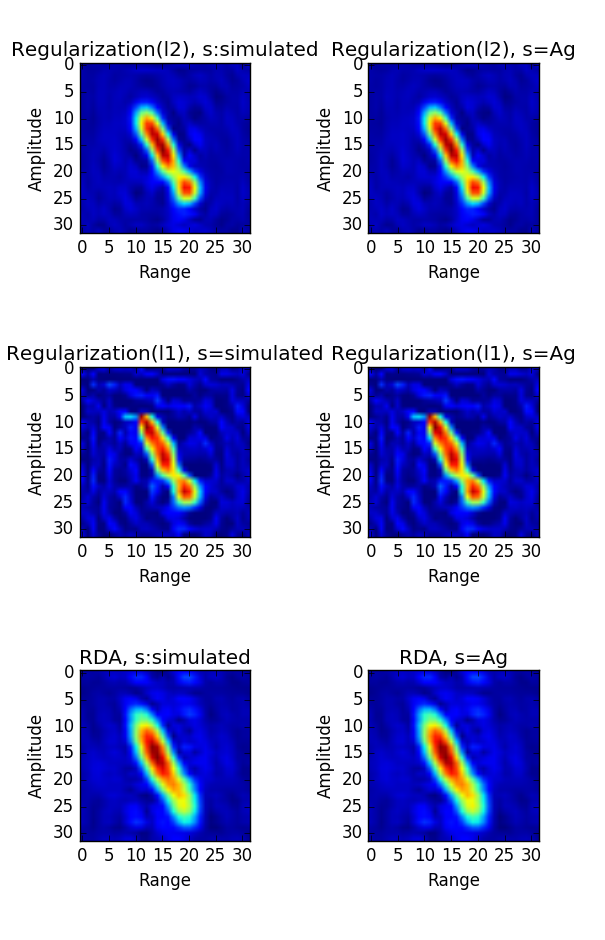
图 4.60 Imaging result of \(\ell_1, \ell_2\) regularization and RDA. \(\lambda=0.001\) , max iter 1000¶
运行时间:
重构误差: