2.2. SAR系统组成¶
2.2.1. 硬件系统¶
2.2.2. 脉冲时序与采样¶
如 图 2.71 与 图 2.69 所示, 设雷达于 \(t_k\) 时刻发射第 \(k\) 个脉冲波束, 脉冲宽度为 \(T_p\). 设经过 \(t_{near}\) 时间, 发射脉冲前边缘于 \(t_{A_k}=t_k+t_{near}\) 时刻到达近地点 \(A\); 经过 \(t_{far}\) 时间, 发射脉冲前边缘于 \(t_{B_k}=t_k+t_{far}\) 时刻到达远地点 \(B\), 前边缘到达远地点的脉冲又经过 \(t_{far}+T_p\) 时间, 其后边缘到达雷达. 雷达接收机在稍早于 \(2t_{A_k}\) 的时刻 \(2t_{A_k} - \delta_{A_k}\) 开始采样, 并于稍晚于 \(2t_{B_k}+T_p\) 的时刻 \(2t_{B_k} + T_p + \delta_{B_k}\) 结束采样, 则采样时间为 \(T_{r} = (2t_{B_k} + T_p + \delta_{B_k}) - (2t_{A_k} - \delta_{A_k})\). 其中, \(\delta_{A_k} > 0, \delta_{B_k} > 0\), \((k=0, 1, \cdots, N_a)\) 为很小的正数, 故采样时间
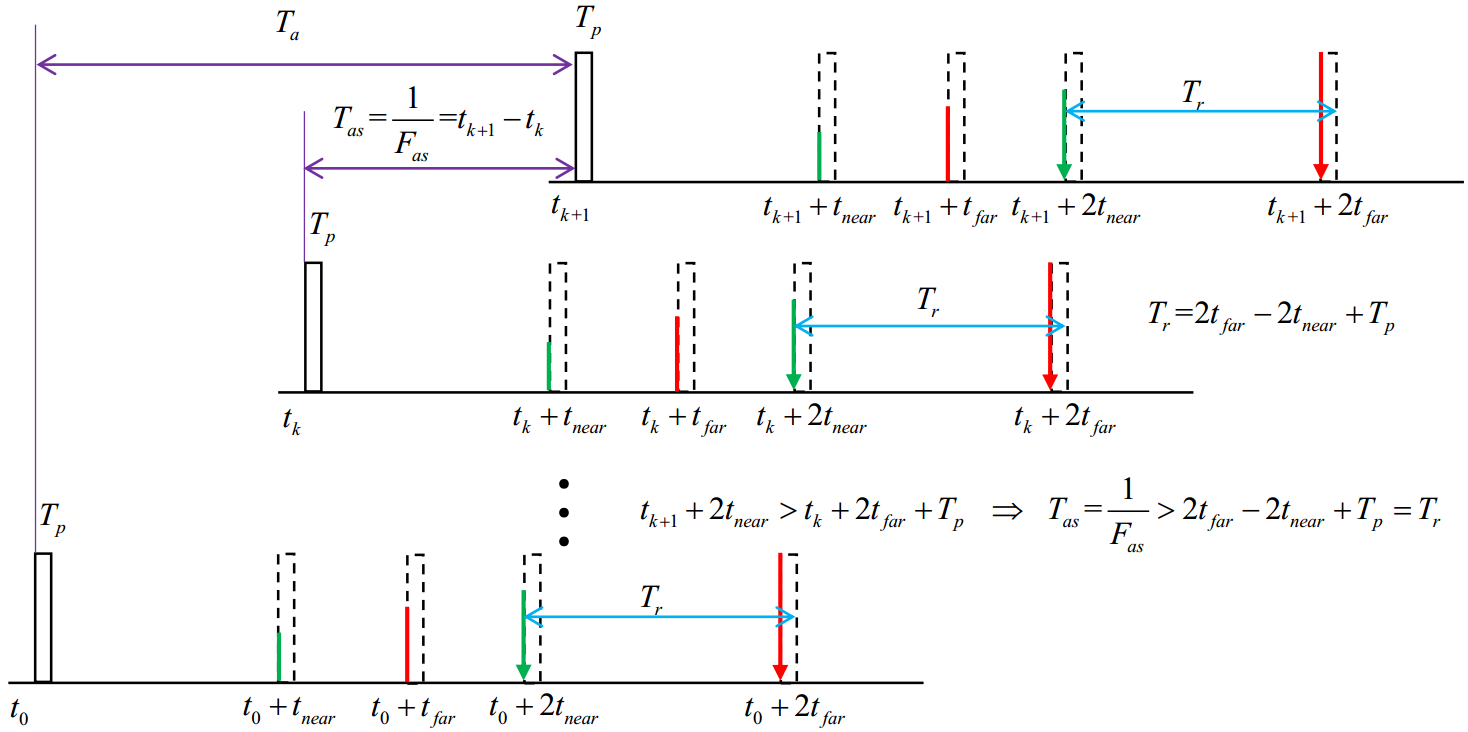
图 2.69 Time sequence of SAR transmitting and receiving pulse.¶
如 图 2.69 所示, 第 \(k+1\) 个脉冲必须在第 \(k\) 个脉冲到达雷达后才可以发射, 因而有
从而有
其中, \(F_{as}\) 为方位向采样频率, \(T_{as}\) 为方位向采样周期, \(T_{r}\) 为距离向采样时间.
2.2.3. 几何建模¶
关键参数计算¶
卫星速度与波束掠过地面的速度¶
如 图 2.70 所示, 地球半径为 \(R_e\), 卫星在距离地面高度为 \(H\) 的高空以速度 \(V_s\) 围绕地球运动, 下视角为 \(\theta_d\), 波束掠过地面的速度为 \(V_g\). 由 图 2.70 中几何关系知 \(x + AB{\tan}\theta_d = R_e + H\), 即
化简后得
式.2.28 的解为
式.2.29 中, 当 \(0 < \theta_d < \pi/2\) 时, 分子取加号; 当 \(π/2 < \theta_d < \pi\) 时, 分子取减号.
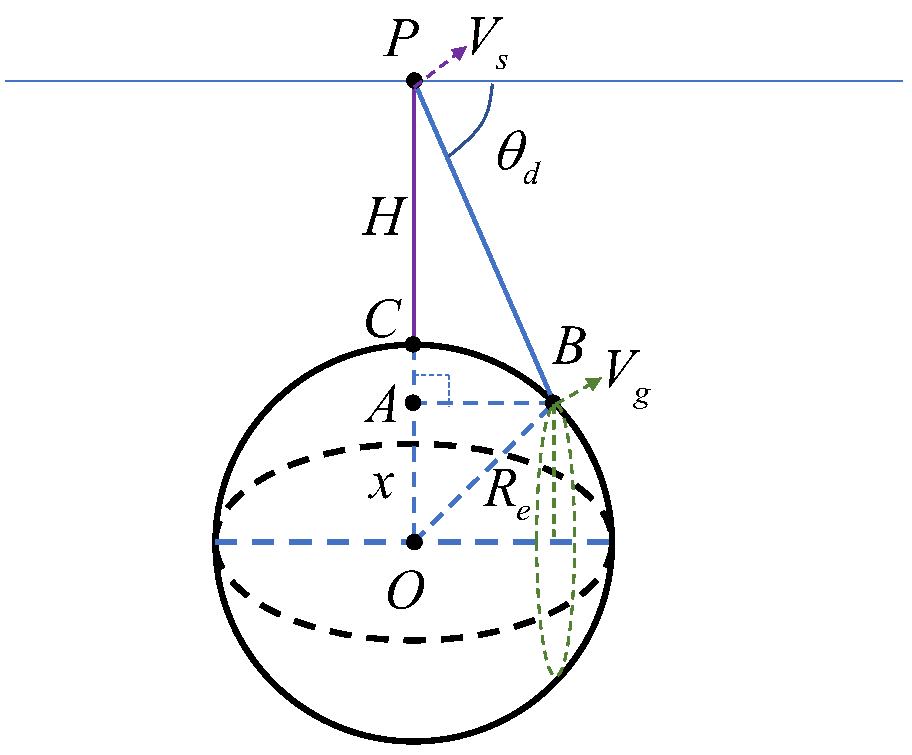
图 2.70 Satellite velocity and beam skimming velocity¶
距离向波束宽度计算¶
根据采样点数 \(N_r\), 采样率 \(F_{rs}\), 平台高度 \(H\) 以及下视角 \(\theta_d\), 可以计算距离向波束宽度 (antenna elevation beamwidth) \(\beta_e\). 如 图 2.71 所示, 由 图 2.71 中几何关系及 式.2.26 得
其中, \(c\) 为光速, \(N_r\) 为距离向采样点数, \(N_p\) 为 \(T_p\) 时间内的距离向采样点数. 式.2.30 代入积化和差 \(\sin \alpha \sin \beta=\frac{1}{2}[\cos (\alpha-\beta) - \cos (\alpha+\beta)]\) 与和差化积公式 \(\sin \alpha-\sin \beta=2 \cos \frac{\alpha+\beta}{2} \sin \frac{\alpha-\beta}{2}\), 式.2.30 化简后得到
即
从而解得
其中, \(a = \frac{c(N_{r}-N_p)}{F_{rs}}\), \(c\) 为光速. 由于 \({\sin}\frac{\beta_e}{2}\in[-1, 1]\), 可以排除一个解.
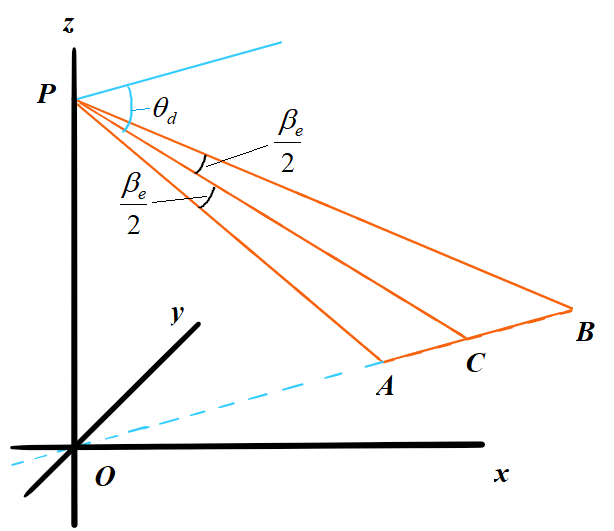
图 2.71 Beam width and footprint geometry in range direction¶